Monitoring Desk
ISLAMABAD: The link between obesity and the brain is a fascinating topic that scientists have only recently begun to explore.
From the size and functionality of the brain to specific neuronal circuits, recent studies have brought to light important aspects of the connection between obesity and the brain.
For instance, researchers published a study earlier this year that found a link between obesity around the stomach area and smaller brain size — specifically, lower gray matter volume.
The findings of another recent study showed that the brain’s prefrontal cortex — an area that is important for complex thinking, planning, and self-control — is less active in people who tend to overeat, which may lead to obesity and weight gain.
Finally, research that appeared only last month identified an array of neurons that can curb overeating when they become active.
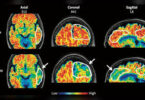
Dr. Ilona A. Dekkers, from the Leiden University Medical Center in the Netherlands, led a team of researchers who used cutting-edge MRI scanning technology to understand the link between obesity and brain structure.
Dr. Dekkers and team reported smaller gray matter volumes in people with obesity, thus solidifying previous research findings. They also found connections with the brain’s form and structure, called its morphology.
The researchers published their findings in the journal Radiology. Dr. Dekkers and her colleagues decided to investigate how obesity might affect the brain because previous studies had found a higher risk of cognitive decline and dementia among people with obesity.
So, the scientists examined brain scans from over 12,000 people who took part in the United Kingdom Biobank Imaging study. The brain imaging techniques that the team used in the study offered insights into the participants’ gray and white matter.
Gray Matter and White Matter of Brain
Describing the brain in very broad terms, this central processing unit consists of an “outer cortex of gray matter and an inner area housing tracts of white matter.” The gray matter is packed with neurons, whereas white matter primarily consists of nerve projections called axons and glial cells.
Gender-Based Differences
In the current study, according to Dr. Dekkers, the team found that “having higher levels of fat distributed over the body is associated with smaller volumes of important structures of the brain, including gray matter structures that are located in the center of the brain.”
Courtesy: (globalvillagespace.com)